

For example, a person experiencing a positive aura may see zig-zag or squiggly lines, flashes, stars, or dots. This is when a person sees something that isn’t actually there.
Understanding the other types of visual disturbances that may accompany a migraine can provide more clarity. Kaleidoscope vision is a component of only one type of visual aura. Other forms of auras include tingling in the hands or face, muscle weakness, and difficulty speaking. About 20% of people who suffer from migraines experience some type of aura, also known as a sensory disturbance. The most common cause of kaleidoscope vision is an ocular migraine, which is a migraine accompanied by visual symptoms. In many cases, visual auras precede headaches and migraines.Įpisodes of kaleidoscope vision usually last between 10-30 minutes, but can persist up to an hour. Visual symptoms like kaleidoscope vision can affect one or both eyes and can occur with or without a headache. A person experiencing kaleidoscope vision may perceive their visual field to be fractured, vividly colored, or scrambled - similar to looking through a kaleidoscope. Kaleidoscope vision is not a stand-alone condition, but rather a visual symptom of migraines or conditions like a stroke or brain injury. Home » Eye Care Services » Neuro-Optometric Rehabilitation » Kaleidoscope Vision What Is Kaleidoscope Vision?
follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. Injury to the carotid or vertebral arteryĪ.D.A.M., Inc.Tumor, mass, or lymph node in the upper chest or lymph node causing pressure on a nerve may cause decreased sweating, a small pupil, or drooping eyelid all on the affected side (Horner syndrome).Seizure (pupil size difference may remain long after seizure is over).Infection of membranes around the brain ( meningitis or encephalitis).Increased intracranial pressure, because of brain swelling, intracranial hemorrhage, acute stroke, or intracranial tumor.Excess pressure in one eye caused by glaucoma.Brain tumor or abscess (such as, pontine lesions).Bleeding inside the skull caused by head injury.Other causes of unequal pupil sizes may include: Other medicines that get in the eyes, including medicine from asthma inhalers, can change pupil size.
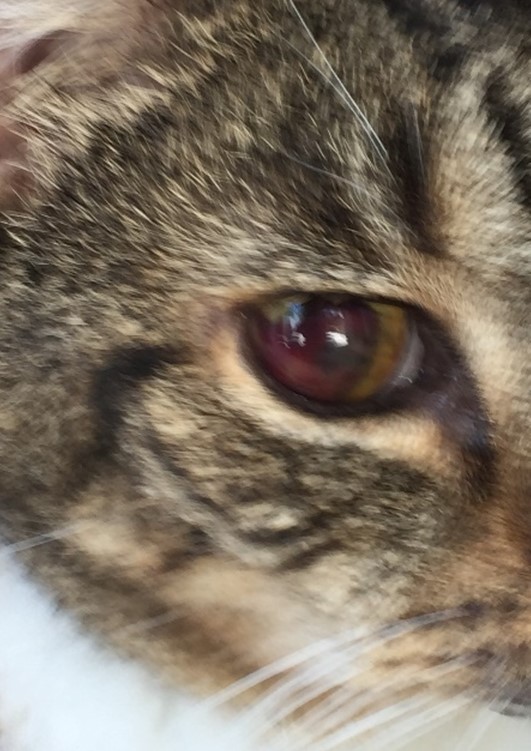
The use of eye drops is a common cause of a harmless change in pupil size.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
